Email: pravin@anandandanand.com • vaishalimittal@anandandanand.com
Website: www.anandandanand.com
By Pravin Anand and Vaishali Mittal, Anand and Anand
“In a progressive country change is constant; change is inevitable.”—
Benjamin Disraeli
 The past few years have seen plentiful developments in the Indian IP regime. The judiciary has consistently delivered landmark decisions in every field of IP, be it patents, copyright or trade marks, and the government has gained widespread global appreciation for its numerous initiatives to strengthen IP, while the legislature has passed new laws that not only prioritise IP disputes (due to their commercial importance), but ensure that they are adjudicated swiftly through specialised forums.
The past few years have seen plentiful developments in the Indian IP regime. The judiciary has consistently delivered landmark decisions in every field of IP, be it patents, copyright or trade marks, and the government has gained widespread global appreciation for its numerous initiatives to strengthen IP, while the legislature has passed new laws that not only prioritise IP disputes (due to their commercial importance), but ensure that they are adjudicated swiftly through specialised forums.
However, these instrumental gains seem to have been lost on authorities ranking India’s performance in comparison with other nations. The Special 301 Report issued by the US Trade Representative (USTR) places India on its priority watch list, while the index published by the Global Intellectual Property Center (GIPC) ranks India 37 out of 38 economies.
Although India does have ground to cover before it can be said to have one of the strongest IP regimes in the world, even with the current IP infrastructure, there are no such glaring drawbacks to deserve such a ranking. In fact, certain facets of legislation, policy and the practice of IP law in India are so unique that they are unmatched anywhere else.
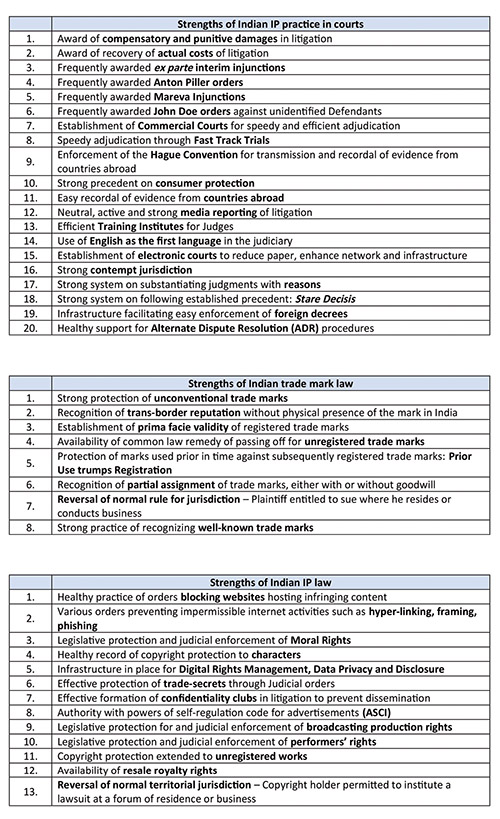
The strengths of Indian IP law
The Commercial Courts Act, 2015 classifies all IP disputes as commercial and thus entitled to swift, expert adjudication. Meanwhile, the executive branch of government dedicated substantial resources to the improvement of IP, with the introduction of campaigns such as Make in India, Digital India, Start-up India along with the National IPR Policy.
Through these campaigns, the government provides incentives to innovators to manufacture, invest and set up businesses here. These efforts ensure that not only is doing business made easier, but grievances of IP holders are given quality adjudication by expert bodies sensitive to their needs and interests, irrespective of their nationality.
Such developments on the judicial front are unprecedented, with the judiciary spearheading the campaign of invigorating IP. Landmark decisions, in sync with internationally established principles, have resulted both in the strengthening of IP, and in exponentially increasing the faith of IP holders in the judicial system.
Various aspects showcasing the true strengths of IP in India are assessed below.
General aspects of IP litigation
It is not only statutory provisions regulating IP, but also the manner in which courts help litigants implement them, that showcase the strengths of the Indian system. The judiciary has single-handedly improved jurisprudence by such leaps and bounds that previously unheard of legal principles have become regular features today.
With an extremely relief-centric approach, the courts have a healthy practice of Anton Piller, Mareva and ex parte injunction orders. Conducting cross-examinations of witnesses through video recordings and setting strictly fixed timelines for trials are some steps that are taken specifically to protect the interests of international entities.
 Trade marks
Trade marks
It can be safely stated that Indian trade mark law can stand its ground against any other regime in the world, in addition to having factors in its kitty which are unique to India.
While trans-border reputation of trade marks and their declaration as being well-known have been established for years now, recent decisions have extended this status to unregistered marks too. Moreover, when only a few regimes confer protection to unconventional trade marks, India does that and a lot more, being one of the few countries to have declared even colour-marks as well-known.
Brand-owners have also been given the liberty to institute lawsuits at those forums where they reside or conduct business. This is a special privilege offered only in trade mark and copyright law, since every other field of law requires one to institute suits at forums where the defendant resides, among other grounds.
Copyright, piracy and trade secrets
The 2013 amendments to the Copyright Act, 1957 led to the implementation of several provisions that strengthened the law and brought it closer to established international practices. Added provisions on the extension of moral rights to authors, mandatory payment of royalty to different entities involved in a copyrighted work, extended protection terms to photographs and other works have bolstered the regime further.
Moreover, the established practice de-hors these amendments had ensured that the menace of counterfeiting and online piracy was well addressed. India has been home to website blocking orders and restraining infringing activities of hyperlinking, meta-tagging, phishing, framing, etc. The fact that these orders were passed at a time when India was warming up to the notion of the internet showcases the constantly proactive approach of the judiciary.
 Patents
Patents
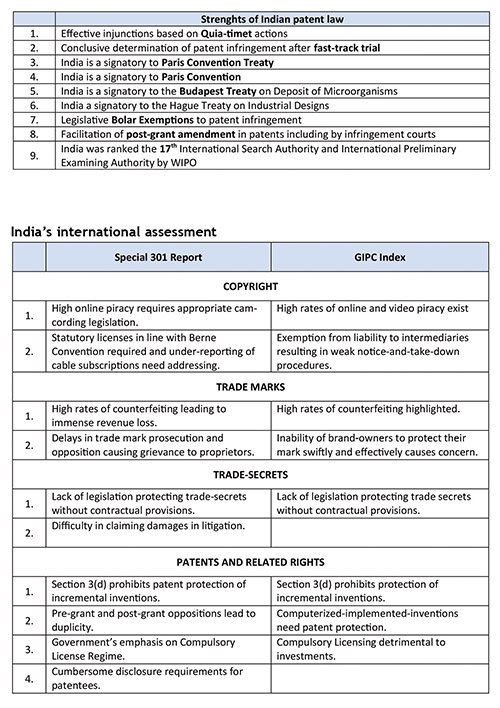
Patent law has grown the most among all fields, with immediate steps being taken to reshape perception whenever it turned sour.
Difficulties caused to patentees due to delays in prosecution of patents saw the judiciary directing the Patent Office to mandatorily increase its workforce and improve resources. Recent trends have seen India rejecting applications for compulsory licenses at the very outset, such as in case of Lee Pharma. Disclosure requirements of international prosecution of patents were heavily toned down and their non-compliance no longer necessarily leads to patent revocation. Moreover, the judiciary has enforced patent rights even in situations where the patentee apprehends sale of infringing products. This concept of quia timet actions, a regular feature in India today, was unheard of previously.
More importantly, India witnessed its first final decisions in contested patent litigation, where a finding of infringement was conclusively given by the judiciary in the Merck and Roche litigation cases. These decisions have clarified that the controversial section 3(d) does not provide a defence to patent infringement and that it is only a patent eligibility criterion.
Geographical indications and plant varieties
India has a very strong infrastructure protecting geographical indications and plant varieties. Besides dedicating specialised legislations for these fields, India is one of the few countries to maintain a database of traditional knowledge. The Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL), containing information on more than two million medicinal formulations, is a tremendous success and has greatly assisted patent examiners while searching for prior art and has also enabled India to bring about the cancellation or withdrawal of 36 patent applications for traditionally known medical formulations.
Executive’s incentives to startups
Against the backdrop of a strengthening IP system, the National IPR Policy, along with other campaigns, offers several incentives to entrepreneurs to ensure that India receives greater investments. Such incentives include reduced fee for patent filings for startups, accelerated examination of patent applications on payment of higher fees, etc.
Interntional analysis of Indian IP: Overlooking its strengths?
While the assessment of the weaknesses that India’s regime suffers from is correct to a large extent, the evaluation of its strengths isn’t. The main areas facing criticism in the 301 Report and the GIPC Index are given in the table above.
India’s assessment
In addition to the table above, the Special 301 Report has critiqued the government’s initiatives as favouring localisation and indigenous products and services.
 Improvements needed in Indian IP law
Improvements needed in Indian IP law
A recent interview by the senior director of IP at GIPC predicted an increase in India’s performance on the Index by 2020. Mere compliance with TRIPS objectives wasn’t found sufficient and India was urged to ensure that its regime employs safeguards in sync with international practices today. Such criticism will undoubtedly paralyse the growth of the Indian regime.
Certain facets warranting legislative and executive action are outlined below:
(i) Trade marks
- Consistency is required on parallel importation to enhance revenue;
- Delays in the prosecution of trade marks need to be reduced.
(ii) Copyright
- Loss of copyright protection on articles registrable under design law (but where registration wasn’t secured) upon production of more than 50 articles needs to be done away with.
- Responsibility of intermediaries for de-listing infringing content must
be tightened.
(iii) Patents
- Either pre-grant or post grant oppositions to a patent must be eradicated;
- Restraints on patentability of inventions imposed by section 3(d) and section 3(k) must be addressed;
- Grant of compulsory licences must depend upon stricter thresholds;
- Prima facie validity of granted patents can be considered;
- Patent term extensions must be facilitated; and
- Disclosure requirements for working of a patent, its international prosecution and consequences of its non-compliance must be relaxed.
Conclusion
The strength of every regime lies in the balance struck between national interests and international expectations, and the past few years have seen India excel at it. Any favour extended to domestic entities by the executive is balanced by the judiciary’s protection of international interests and vice versa. India’s regime is robust not only when compared to its past performance, but also in comparison to the existing regimes of several countries.
Evaluation of the regimes of countries by ranking agencies such as USTR and the GIPC have a significant impact since they help rights-holders invest in regimes based upon such evaluation. A true and fair evaluation of India’s regime is crucial to India to help prevent loss of investments from misconceptions.
Therefore, future assessment of Indian IP by GIPC, USTR or any other agency must definitely take into account its numerous strengths, to enable the world to see it is a robust system. Not the strongest of the strongest, but certainly not the weakest!